Introduction to Digital Signatures
In the digital age, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents is crucial. So, Digital signatures play a vital role in achieving this by providing a way to verify the identity of the sender and detect any alterations to the content of a message or document. In this article, we’ll delve deep into the world of digital signatures, exploring how they work, their applications, and their importance in modern communication and security systems.
Understanding Digital Signatures
At its core, a digital signature is a cryptographic technique that uses a combination of public and private keys to verify the authenticity and integrity of a message or document. Moreover, The process begins with the sender generating a unique hash (or digital fingerprint) of the message using a cryptographic algorithm. This hash is then encrypted using the sender’s private key, creating the digital signature. So, The recipient can use the sender’s public key to decrypt the signature and verify the hash. It ensures that the message has not been tampered with and is from the purported sender.
Digital Signature Process Diagram
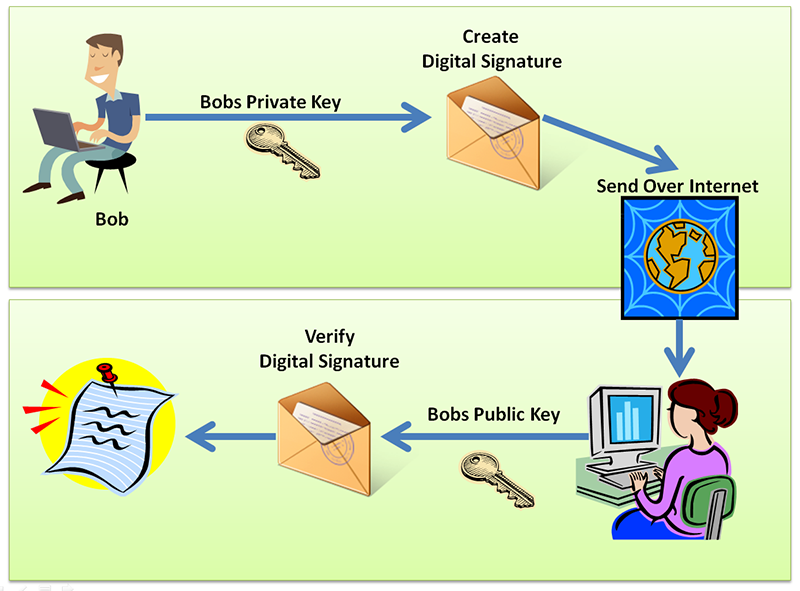
Real-World Examples
Digital signatures are widely used in various applications, including email communication, software distribution, and document authentication. For example, in email communication, digital signature helps verify the identity of the sender. It also ensures that the message has not been altered during transmission. Similarly, in software distribution, a digital signature is used to confirm the authenticity of software updates and patches, protecting users from malicious software.
Benefits and Importance of Digital Signatures
Digital signatures offer several key benefits, including:
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of the sender.
- Integrity: Ensuring that the message has not been altered.
- Non-repudiation: Preventing the sender from denying sending the message.
- Efficiency: Streamlining document signing processes and reducing paperwork.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital signature plays a vital role in ensuring the security and integrity of electronic communication. So, By understanding how they work and their benefits, individuals and organizations can leverage a digital signature to enhance the security of their digital assets and communications.
Learn more at SecureWell.
